Detailed Explanation and Guide For Third-Party Cookies
Third-party cookies are critical and Google was about to deprecate them in 2024 because they were getting a bad name for tracking and tracing but in the end Google capitulated and now we can safely say that “3rd Party Cookies are here to stay”, yet their role is often misunderstood. These cookies are set by domains other than the one a user is currently visiting. They are embedded through elements like advertisements, social media buttons, or tracking pixels on the host website. The ability of third-party cookies to track user activity across different websites makes them invaluable for advertisers and data analysts. However, this tracking capability has also led to significant concerns over user privacy.
The technical functionality of third-party cookies hinges on their ability to collect data on users without their direct interaction with the cookie-setting domain but rather from landing on a different website. This data is typically used for purposes such as targeted advertising, where the information gathered about a user’s browsing habits is used to serve personalized ads. For instance, if a user frequently visits sports-related websites like ESPN, third-party cookies might track this behavior and ensure that the user sees sports-related ads for Fanatics gear even when they are on unrelated websites.
The Mechanism of Third-Party Cookies
Third-party cookies work through HTTP requests made by a user’s browser. When a user visits a website, the browser requests the content from the server hosting the site. If the website includes third-party elements (such as ads or social media plugins), the browser will also make requests to the third-party servers. These third-party servers then respond by setting cookies in the user’s browser, which can be accessed on subsequent visits to any site that includes elements from the same third party.
The data stored in these cookies typically includes unique identifiers that allow the third party to recognize the user across different sessions and websites. This ability to track users across multiple sites is what makes third-party cookies so powerful for advertising purposes but also raises significant privacy concerns.
The Global Discussion on the Safety of Third-Party Cookies
The Argument for Allowing Third-Party Cookies
While third-party cookies have been demonized in some circles, it’s important to understand that they are not inherently harmful. They are simply tools that can be used for both beneficial and potentially harmful purposes. In many cases, third-party cookies enhance the online experience by enabling personalized content and relevant advertisements.
For instance, when a user consistently receives ads for products or services they are genuinely interested in, it can enhance their browsing experience by providing value. Moreover, businesses rely heavily on the data provided by third-party cookies to optimize their marketing strategies, improve product offerings, and ultimately provide better services to consumers.
Furthermore, the security of third-party cookies has been significantly improved over the years. Modern browsers enforce strict security measures that limit the potential misuse of these cookies. For example, the introduction of the SameSite attribute allows websites to specify when cookies should be sent with cross-site requests, thereby reducing the risk of cross-site request forgery (CSRF) attacks.
The Importance of Encryption
Another crucial aspect of third-party cookie safety is encryption. When data is transmitted over HTTPS, the information in the cookies is encrypted, making it much harder for malicious actors to intercept and misuse the data. This encryption ensures that even if the data is accessed by an unauthorized party, it would be nearly impossible to decrypt without the proper keys.
Detailed Importance of Consent Management Platforms (CMPs)
Legal Frameworks and CMPs
Consent management platforms (CMPs) have become a cornerstone of online privacy, particularly in the wake of stringent regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the CPRA or previously The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. These regulations require websites to obtain explicit consent from users before collecting or processing their data, including through the use of third-party cookies. In case you didn’t know you can use the consent management software from Captain Compliance to help automate your data privacy compliance journey.
CMPs facilitate compliance with these legal requirements by providing mechanisms for obtaining and managing user consent. They offer features such as customizable consent banners, preference management, and detailed logging of consent actions, which are essential for demonstrating compliance during regulatory audits.
Enhancing User Trust through Transparency
Beyond legal compliance, CMPs play a crucial role in building and maintaining user trust. By clearly communicating how user data will be used and offering easy-to-understand options for managing cookie preferences, CMPs empower users to take control of their online privacy. This transparency not only enhances the user experience but also fosters a more trustworthy and ethical digital ecosystem.
For example, a well-implemented CMP allows users to see exactly which third-party cookies are being used on a site, what data is being collected, and for what purposes. Users can then make informed decisions about whether to allow these cookies, reject them, or customize their preferences. This level of control and transparency is critical in addressing the privacy concerns associated with third-party cookies.
Expanded Steps to Unblock Third-Party Cookies
Browser-Specific Guidelines
While the steps to unblock third-party cookies have been briefly covered, a more detailed look at the process across different browsers can provide additional clarity:
- Google Chrome:
- Step 1: Click on the three vertical dots in the top-right corner and select “Settings.”
- Step 2: Scroll down and click on “Privacy and security.”
- Step 3: Under “Cookies and other site data,” choose either “Allow all cookies” or “Block third-party cookies in Incognito” depending on your preference.
- Step 4: Restart the browser to apply the changes.
- Mozilla Firefox:
- Step 1: Click on the three horizontal lines in the top-right corner and select “Preferences.”
- Step 2: Navigate to the “Privacy & Security” panel.
- Step 3: Under “Enhanced Tracking Protection,” select “Standard” or “Custom” and adjust the cookie settings accordingly.
- Step 4: Close and reopen the browser to activate the new settings.
- Safari:
- Step 1: Open the Safari menu and choose “Preferences.”
- Step 2: Click on the “Privacy” tab.
- Step 3: Uncheck “Prevent cross-site tracking” to enable third-party cookies.
- Step 4: Close the Preferences window and restart Safari.
These steps illustrate how unblocking third-party cookies can be a straightforward process, although it is important to understand the potential implications for privacy and security.
Google Reversing Decision Regarding Third-Party Cookies
Industry Reactions and Implications
Google’s initial announcement to deprecate third-party cookies sent shockwaves through the digital advertising industry. Many advertisers, marketers, and publishers expressed concerns about the potential impact on their ability to deliver personalized content and measure ad effectiveness. The decision to delay the deprecation reflects Google’s acknowledgment of these concerns and its commitment to finding a balanced solution.
The delay has allowed the industry to prepare for a future without third-party cookies by exploring alternative tracking methods, such as first-party data and contextual advertising. These methods focus on targeting users based on the content they are engaging with, rather than tracking their behavior across multiple sites. In the end in Q3 in 2024 they came out and said 3rd party cookies are here to stay and they will not be deprecating after all.
The Future of Tracking Technologies
As Google continues to develop its Privacy Sandbox initiative, the future of tracking technologies remains uncertain. However, it is clear that any future solution will need to strike a delicate balance between protecting user privacy and maintaining the functionality of the online advertising ecosystem.
Expanded Analysis of Pixel Tracking
Advantages and Limitations of Pixel Tracking
Pixel tracking offers several advantages over third-party cookies, particularly in the context of user privacy. Since tracking pixels do not store data on the user’s device, they are less likely to be blocked by browsers or ad blockers. This makes them a more reliable tool for tracking user behavior, especially in an environment where cookies are increasingly restricted.
However, pixel tracking is not without its limitations. Unlike cookies, which can store data over multiple sessions, tracking pixels only collect data during the session in which they are loaded. This means that they are less effective for long-term tracking and cannot provide the same level of detailed user profiles as third-party cookies.
Use Cases for Pixel Tracking
Pixel tracking is commonly used in email marketing to track open rates and user engagement. When a user opens an email containing a tracking pixel, the pixel sends a request to the server, allowing the marketer to know that the email was opened and, in some cases, what actions the user took afterward.
In addition to email marketing, pixel tracking is also used for website analytics. By embedding tracking pixels on key pages of a website, businesses can gain insights into how users navigate their site, what content they engage with, and where they drop off in the conversion funnel.
First-Party vs. Third-Party Cookies
In-Depth Comparison
While first-party and third-party cookies serve different purposes, it is important to understand the specific contexts in which each is most effective:
- First-Party Cookies:
- Purpose: First-party cookies are primarily used to enhance the user experience on the website that sets them. For example, they can remember user preferences, login information, and items in a shopping cart, making subsequent visits to the site more seamless.
- Privacy: Since first-party cookies are only accessible by the domain that set them, they pose fewer privacy concerns compared to third-party cookies. Users are generally more accepting of first-party cookies because they provide direct benefits related to the site they are visiting.
- Third-Party Cookies:
- Purpose: The primary function of third-party cookies is to enable cross-site tracking for advertising and analytics purposes. By following users across multiple sites, third-party cookies allow advertisers to build detailed profiles and deliver highly targeted ads.
- Privacy: Third-party cookies have been at the center of privacy debates because they enable the tracking of user behavior across the web without the user’s direct knowledge or consent. This has led to growing calls for more privacy-friendly alternatives.
Expanded Section on Third-Party Cookie Examples
Real-World Implementations
To provide a more comprehensive understanding of how third-party cookies are used in practice, let’s examine several real-world examples:
- Google AdSense: One of the most widely used advertising platforms, Google AdSense relies heavily on third-party cookies to deliver targeted ads to users based on their browsing history. By placing cookies on millions of websites across the internet, AdSense can track user behavior and serve relevant ads on partner sites. Now you can see why they didn’t want to give up on third-party cookies.
- Facebook Pixel: The Facebook Pixel is a piece of code that website owners can add to their site to track user interactions and measure the effectiveness of their Facebook ads. When a user visits a site with the Facebook Pixel installed, a third-party cookie is set, allowing Facebook to track the user’s behavior and use that data to optimize ad delivery.
- Google Analytics: Google Analytics uses third-party cookies to collect data on how users interact with websites. This data is used to generate reports on traffic, user behavior, and conversions, providing businesses with valuable insights into the effectiveness of their online presence.
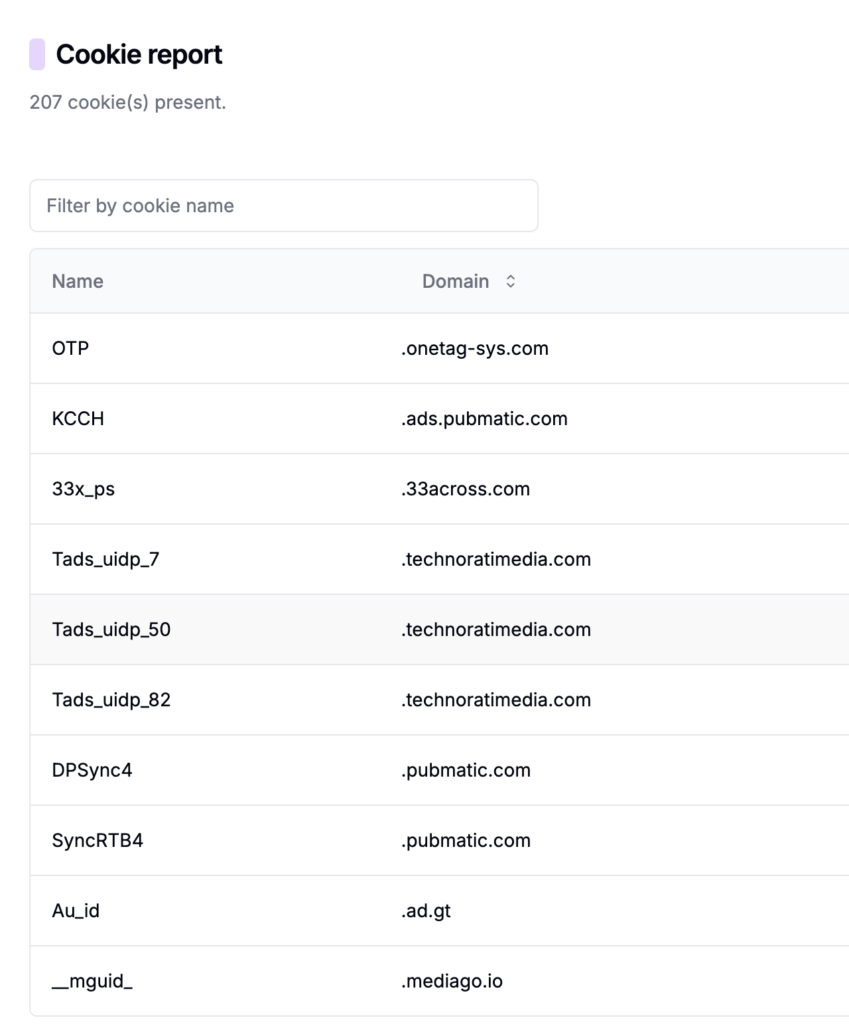
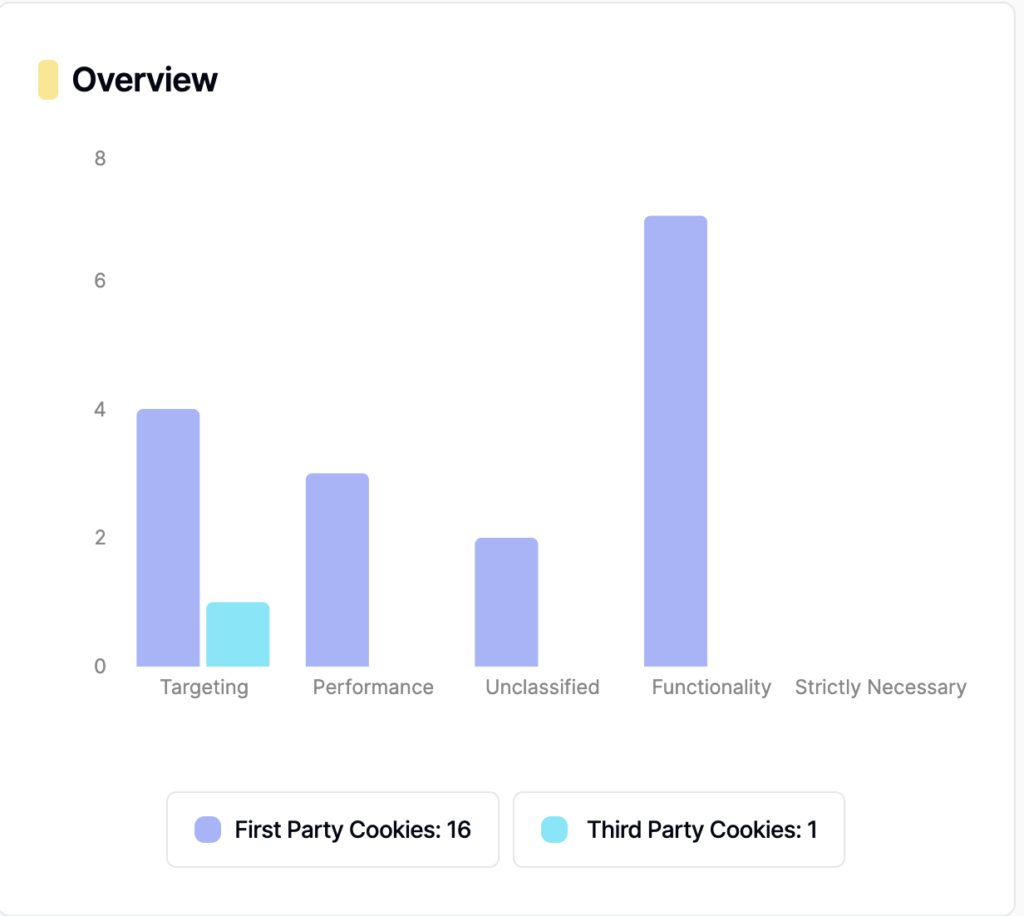
How to Figure Out Which Third-Party Cookies Are On a Website
Mechanisms for Acquiring Third-Party Cookies Include Using our Free Cookie Scanner
There are several mechanisms through which third-party cookies are acquired, each serving different purposes:
- Ad Impressions: When a user sees an advertisement on a website, the third-party server hosting the ad will typically set a cookie on the user’s device. This cookie allows the advertiser to track the user’s interactions with the ad and any subsequent actions they take, such as clicking on the ad or making a purchase.
- Social Media Embeds: Websites often include social media embeds, such as Like or Share buttons, which are served by third-party domains like Facebook or Twitter. When a user interacts with these embeds, third-party cookies are set, allowing the social media platform to track the user’s activity.
- Third-Party Widgets: Many websites use third-party widgets to provide additional functionality, such as live chat, weather updates, or stock tickers. These widgets often come with third-party cookies that track user interactions and collect data for analytics or advertising purposes.
Benefits of Third-Party Cookies
Enhanced Targeting and Personalization
One of the primary benefits of third-party cookies is their ability to deliver highly targeted and personalized content to users. By tracking users across multiple sites, third-party cookies enable advertisers to build detailed profiles that include users’ interests, behaviors, and preferences. This allows for more effective targeting, ensuring that users see ads that are relevant to them, which can lead to higher engagement and conversion rates.
Cross-Platform Consistency
Third-party cookies also provide a consistent experience across different platforms and devices. For example, if a user logs into a service on their desktop and then accesses the same service on their mobile device, third-party cookies can help maintain a seamless experience by remembering the user’s preferences and settings.
Security Risks of Third-Party Cookies
Advanced Threats
The security risks associated with third-party cookies are not limited to privacy concerns. There are also more advanced threats that can exploit vulnerabilities in third-party cookies:
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Third-party cookies can be exploited through cross-site scripting attacks, where malicious scripts are injected into trusted websites. If a third-party cookie is not properly secured, it could be used to execute harmful code on the user’s device, leading to data theft or other malicious activities.
- Cookie Hijacking: If a third-party cookie is transmitted over an unencrypted connection, it could be intercepted by an attacker through a man-in-the-middle attack. This would allow the attacker to hijack the user’s session and gain unauthorized access to their accounts or personal information.
- Malvertising: Malicious advertisements (malvertisements) that contain harmful code can be served through third-party cookies. When a user interacts with a malvertisement, the malicious code can exploit vulnerabilities in the browser or the user’s device, leading to the installation of malware or other security breaches.
So Are Third-Party Cookies Good or Bad?
Third-party cookies are a complex and multifaceted technology that plays a crucial role in the modern digital landscape. While they offer significant benefits in terms of targeting, personalization, and cross-platform consistency, they also pose considerable privacy and security risks. As the industry continues to evolve, with Google delaying and then cancelling the deprecation of third-party cookies and exploring new tracking technologies, it is clear that a balanced approach is necessary. Consent management platforms like the one here at Captain Compliance, pixel tracking, and other emerging solutions will be critical in ensuring that the digital ecosystem remains both effective and respectful of user privacy. The future of third-party cookies has been locked in and their impact on the internet as we know it is undeniable.