
The Personal Information Protection Law is the most significant data protection regulation in effect in China. The law outlines several data privacy requirements, including ensuring Chinese residents have certain PIPL data subject rights.
The data subject rights outline what parts of data processing consumers should be able to control and how businesses must respond to their requests. The purpose of this article is to help your business navigate the challenging requirements of the PIPL.
We will cover the PIPL data subject rights in detail, other rights that consumers have, exemptions, and penalties businesses face if found non-compliant.
Let’s get started.
Key Takeaways
The Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) is China’s foremost data protection law. Any business that processes consumers’ personal information or sensitive PI in China is subject to its regulations.
The PIPL includes a specific set of data subject rights, including the following: right to be informed, right to restrict and refuse, right of access and portability, right to rectify, right to delete, right to explanation, right to automated decisions, right of the deceased, and the right to convenience.
The only exemptions to the authority of the PIPL are businesses that collect anonymized data, data compiled by government or legal bodies, and data collected personally.
What is the PIPL?
What is the PIPL (1).jpg

China enacted the Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) to protect consumers’ personal data and personal information. The law regulates data processing by businesses and creates a standard of data privacy for anybody in China.
Many compare the PIPL to the General Data Protection Regulation in Europe, but the two fundamentally differ. The PIPL has unique compliance requirements for businesses to follow when processing consumers’ personal data, including its own rules on consent and security.
One part of the PIPL that sets it apart from other data protection laws is its requirement for a Chinese representative and extra stringent cross-border data transfer rules. They also impose some of the most severe fines on any business that does not comply with its regulations.
Who Does the PIPL Apply to?
The PIPL has a broad scope of control over businesses worldwide. Your business is subject to the PIPL if it processes the personal data of any consumer in China. The law applies even if your business has no physical presence in China.
Businesses that sell goods or services to consumers in China internationally and process their personal information are subject to the PIPL. As an additional security measure, the PIPL has specific data localization requirements for international data processing.
PIPL Data Subject Rights
PIPL Data Subject Rights.jpg
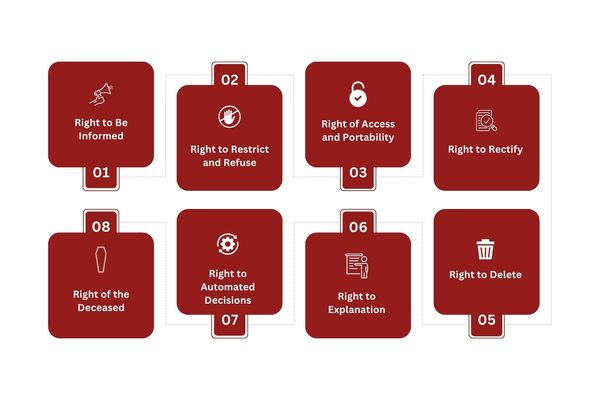
One of the requirements of the PIPL is that businesses provide specific rights to data subjects. Your business must understand and make these rights apparent to all consumers to ensure compliance with the PIPL.
Right to Be Informed
The first data subject right is outlined in Article 17 of the PIPL. According to Article 17, businesses must inform consumers of the following before processing their personal information
The name and contact info of the business/third party that processes the data
Why and how does the business collect personal data, what type of data they collect, and how long they will retain the data
How data subjects can exercise their rights
Any additional information that is required by other laws and regulations
Your business is also required to inform data subjects of any changes in the contents of their data.
Right to Restrict and Refuse
Article 44 of the PIPL grants consumers the right to control and decide on the processing of their personal information. This control includes the ability to refuse anybody from processing their information.
Right of Access and Portability
Article 45 allows consumers to request a copy of their personal information anytime. Businesses are required to provide a copy in a timely manner.
This article also grants consumers the right to request a transfer of their personal information to a different data processor.
Only data handlers who work in the Chinese government or branches of law are exempt from this requirement.
Right to Rectify
Article 46 grants consumers the ability to request your business corrects or adds to their personal information. Upon request, your business is required to make the corrections in a timely manner.
Right to Delete
Article 47 describes the circumstances where a business must delete a consumer’s personal information. If they do not delete the information, consumers are granted the right to request the deletion. Businesses must delete the data under the following circumstances.
The purpose of collecting the data has been achieved or not achieved, or the data is no longer necessary for the purpose
Your business stops providing a good or service, or the agreed retention period of the data has passed
The data subject withdrawals their consent
Your business violated a law, regulation, or agreement regarding personal information processing
Other circumstances outlined in separate laws or regulations
Right to Explanation
Article 48 allows consumers to request an explanation of data processing rules and regulations. Your business is required to provide an explanation in plain language and without charge.
If consumers are unsatisfied with your response or require further clarification, they have the right to bring their concerns to relevant government departments for handling.
Right to Automated Decisions
Article 24 grants consumers the right to request an explanation of any automated decisions that affect the processing of their personal information. Consumers maintain the right to disallow any of these decisions if they so choose.
Your business must follow these requirements and provide data subjects with clear, accessible methods for exercising their rights.
Failure to comply can result in penalties and fines under the PIPL. It is important to regularly review your processes and policies related to data subject rights to ensure compliance with the ever-changing regulations surrounding personal information protection in China.
Right of the Deceased
Article 49 allows the near relatives of a recently deceased data subject to view, copy, correct, or delete the deceased’s personal information unless the deceased states explicitly otherwise before their passing.
This right is meant to protect the privacy and dignity of deceased individuals. Your business must respect this right and handle any requests from near relatives in a timely manner.
Other PIPL Data Subject Rights
Other PIPL Data Subject Rights.jpg
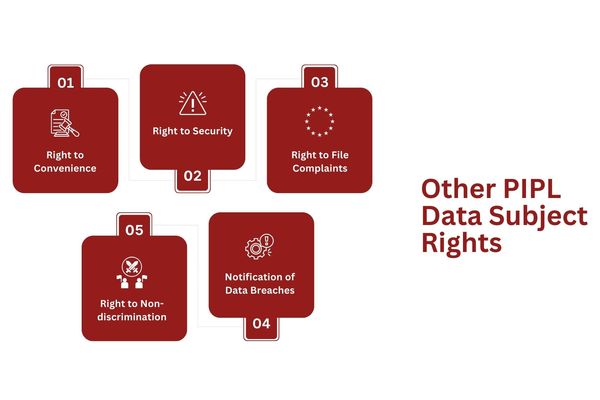
Chinese residents are granted additional rights through other laws and regulations. While these are not stated explicitly in the PIPL, your business should provide them all the same to ensure your continued PIPL compliance.
Right to Convenience
Article 50 states that your business must provide an easily accessible function allowing data subjects to exercise any of the abovementioned rights.
If, for any reason, your business refuses, you must explain why. Upon refusal, a consumer also has the right to form a lawsuit against your business.
Right to Security
Several articles in the PIPL state that your business must provide sufficient safety mechanisms for the data you handle.
Businesses must implement sufficient data security measures to prevent data breaches and protect consumers’ information. Your business can outsource compliance to Captain Compliance to ensure your business meets PIPL security standards.
Right to File Complaints
Consumers maintain the right to file a complaint against your business if they feel their data privacy was violated in any way. Complaints can turn into legal action, resulting in varying levels of punishment for your business.
You could face warnings, demands to update your security standards, significant fines, or even imprisonment in the most severe cases.
Notification of Data Breaches
In the case of a breach, your business must notify all subjects whose data was exposed and the authorities. Your response/notification time and actions to respond to the breach must be up to standard.
Right to Non-discrimination
Any prerequisites or requirements set by your business can’t limit the rights of Chinese citizens. Your business is legally required to grant all rights and privileges to consumers without discrimination.
This includes not denying goods or services, charging different prices, and providing a lower level of service based on the exercise of their data subject rights.
What Are the PIPL Exemptions?
Although the PIPL has a vast range of authority over businesses worldwide, there is a select set of exceptions for businesses. If your business falls under one of the following categories, you may be exempt from specific requirements of the PIPL.
Anonymized Data
If your business processes data that excludes any information that traces back a consumer’s identity, you are not required to follow the PIPL. Anonymization already provides a certain level of security for a consumer by making it challenging to associate data with a specific person.
Government Activities
Any governmental or legal body that collects personal information is not subject to the PIPL. This exemption applies to national government surveys, databases, and personnel authorities.
Personal Affairs
The final exception is for those collecting and processing information for personal matters, such as within a family or in private social relationships. This exemption does not cover businesses that process personal data for profit, and the PIPL will still apply to these organizations.
It is essential to note that even if your business falls under one of these exemptions, you may still be required to comply with specific provisions and obligations outlined in the PIPL. It is best to consult a legal professional like Captain Compliance for guidance on your particular situation.
What Happens if You Aren’t Compliant with the PIPL?
The PIPL contains relatively severe consequences compared to other data protection regulations. The maximum fine for violating the PIPL is 50 million RMB ($7 million) or up to 5% of a business’s annual income.
Receiving a PIPL fine can also hurt a business’s social credit score if in China. This will make it difficult for businesses to be approved for loans or make necessary purchases for regular operations.
In addition, a business can face a damaged reputation amongst consumers. A PIPL violation creates the image of inadequate or lackluster data security and will make consumers less likely to trust your business with their information.
Suppose a consumer decides to bring legal action against your business; the scale of punishments changes. Fines from a lawsuit have no set limit and can range from thousands to millions of dollars, depending on the severity.
Captain Compliance can help your business create an effective compliance plan to remain aligned with PIPL and avoid these harmful fines. We offer a full suite of compliance solutions and services to handle all your business’s compliance needs.
Closing:
The PIPL poses strict regulations on any businesses that process the personal information of anybody in China. Given the broad reach and severity of fines imposed by the PIPL, your business needs to be informed of the PIPL and its standards.
Your business should research and implement all data subject rights listed in the PIPL to remain compliant and avoid significant consequences. Our team of compliance professionals at Captain Compliance can help you do just that.
Our experts have years of experience, and we have the best compliance solutions for your business to handle all of your compliance needs so you don’t have to. Get in touch today!
FAQs
What are data subject rights?
Data subject rights are the privileges businesses must grant consumers whose personal information they process.
In the case of PIPL, businesses must provide certain PIPL rights like the right to be informed, right to restrict and refuse, right of access, and portability, among others.
Want to learn more about PIPL requirements? Click here to find out.
Who is subject to the PIPL?
Any business that processes the personal information of anybody in China is subject to the PIPL. Even if your business is not physically located in China, if you collect data from somebody in China while selling a good or service, you fall under the PIPL’s regulation.
Want to know if you’re potentially subject to the PIPL? Get in touch with us today to find out.
Who enforces the PIPL?
The Cyberspace Administration of China (CAC) is responsible for enforcing the PIPL and administering warnings and fines for violators. Consumers may also submit complaints to the CAC.
Want to avoid fines from the CAC and complaints from consumers? Check out our complete PIPL checklist here.
What are the fines for not complying with the PIPL?
Your business could be subject to warnings, suspension of operations, or varying fines depending on the severity of your violation. The typical fine is up to 1 million RMB or around $140,000. Depending on the severity, though, it can go up to 50 million RMB ($7 million) or 5% of a business’s annual income.
Here’s what non-compliance can cost you if you violate the PIPL.
What is considered personal data in China?
Under the PIPL, personal data is defined as any information a business collects that relates to or is recorded under the identity of any person(s) in China.