Dark patterns or deceptive design tactics that manipulate consumer decisions which has become a critical focus for the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in recent years. Companies using these manipulative interfaces, especially in consent banners related to data privacy, face substantial legal and financial risk. Did you know that there have been more notable FTC fines and an increase in enforcement trends in the last 5 years then the last 20 years? We provide you the best practices for compliance in our never ending and evolving regulatory landscape.
Captain Compliance ensures businesses avoid FTC scrutiny and penalties for dark or deceptive patterns by embedding transparent, user-friendly consent banner tools directly in our compliance solutions dashboard and if you let us we will gladly set it up for you free of charge! Our platform’s consent management system presents users with clear, equal “Accept” and “Decline” choices, eliminates pre-ticked consent boxes, and maintains simple, direct language throughout the consent process. By automating banner configurations in line with evolving FTC, CPRA, and global privacy regulations, Captain Compliance reduces legal and financial risks for clients and builds trust with website visitors by making privacy choices accessible and honest.
Additionally, Captain Compliance regularly audits consent flows to guarantee that opting out actually disables tracking and data collection, a common regulatory pitfall for many organizations. Our data privacy software solutions and systems are updated to reflect changes in regulations and industry best practices, ensuring that client banners always deliver true choice and clear information. With detailed reporting, policy templates, and hands-on privacy support, Captain Compliance empowers organizations to demonstrate compliance and proactively avoid costly enforcement actions related to dark patterns and deceptive UX.
What Are Dark Patterns?
Dark patterns are user interface designs that intentionally trick or coerce users into actions they may not intend, such as sharing personal data, subscribing to unwanted services, or agreeing to ambiguous privacy terms. Examples include hiding “Decline” options, pre-ticked consent boxes, and complex opt-out processes.
The FTC regards these practices as unfair or deceptive under Section 5 of the FTC Act, especially when they impair users’ autonomy or decision-making in areas like cookie consent and privacy choices. Key state laws—such as the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) and Colorado Privacy Act (CPA)—also specifically prohibit obtaining consent through dark patterns.
Below is an image of a dark pattern example for a consent banner where the colors are not the same and the Accept is bright blue to entice a click.
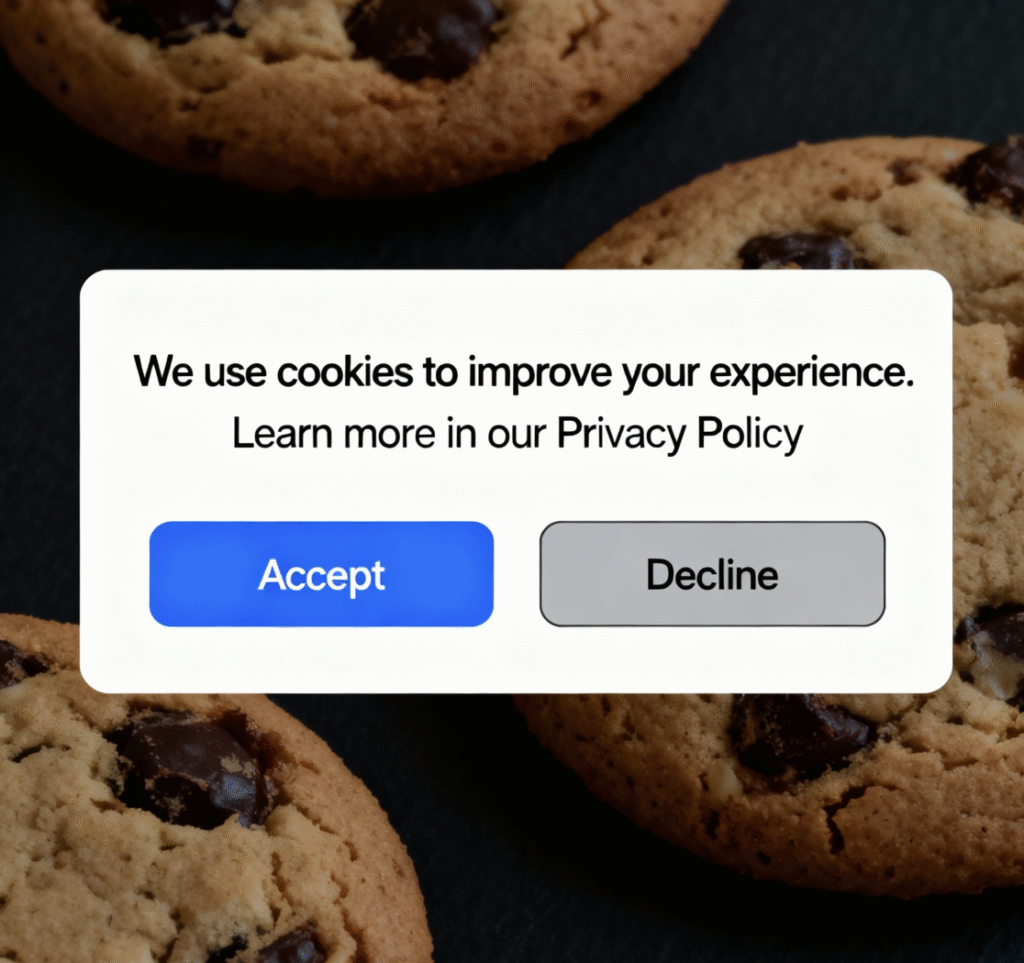
FTC Fines for Dark Patterns: Cases and Trends
- Amazon – The FTC fined Amazon $30 million for employing manipulative tactics (including countdown timers and obstructive cancellation paths) in Prime subscriptions, with findings applicable to deceptive consent flows.
- Publishers Clearing House (PCH) – PCH agreed to an $18.5 million settlement after allegations it used confusing interfaces and misleading consent methods in sweepstakes entries.
- Healthline – California AG imposed $1.55 million in penalties over cookie consent banners that failed to respect user opt-out choices for advertising cookies.
- General Cases – FTC reports show increasing enforcement against companies who present consent options asymmetrically, obscure opt-out paths, or employ “illusory” choices in privacy settings.
These cases illustrate the FTC’s aggressive approach: any consent flow that leverages design tricks to nudge more data sharing or makes opt-out difficult is at risk for investigation and sizable penalties.
Deceptive Patterns and Data Privacy Compliance
Beyond the FTC Act, state laws like CPRA explicitly invalidate user consent obtained via dark patterns, making such practices illegal and subject to regulatory action.
The CPRA and CPA require that banners offer clear, equally prominent choices to “Accept” or “Decline” data use, avoid manipulative language, and eliminate unnecessary opt-out friction. This means websites must not bury the rejection button, use double negatives, or require extra steps to opt-out.
Most states can fine violators up to $7,500–$50,000 per violation, depending on the location and scope of the infraction. The FTC and state AGs are empowered to investigate and enforce these requirements, sometimes pursuing daily penalties until compliance is met.
Best Practices for Consent Banner Compliance
- Present “Accept” and “Decline” choices equally, with clear, prominent buttons. Honda had a banner using the industry leader OneTrust and was hit with a $632,500 fine by the CPPA for misconfigurations.
- Use simple, direct language; avoid legalese or confusing terms.
- Do not use pre-checked boxes for consent; require an affirmative, explicit action.
- Ensure opt-out processes are one-click or as simple as the opt-in process.
- Audit banners regularly to confirm they technically disable tracking if users decline consent.
- Monitor regulatory updates—states are rapidly expanding specific prohibitions and enforcement powers.
FTC and state regulators show zero tolerance for manipulative consent flows
The FTC and state regulators show zero tolerance for manipulative consent flows that undermine user autonomy. Legal and reputational risks from fines, penalties, and enforcement actions are escalating. Transparent, user-friendly consent practices are not just ethical—they are essential for compliance, brand trust, and risk management in today’s privacy landscape.