
Privacy laws worldwide may differ in scope and approach, but each provides consumers or data subjects with several rights, including the right to make a Subject Access Request (SAR). Under the GDPR, a data subject can request a SAR, a copy of their data with the controller.
This article will explain a SAR request and the steps to handle it as a business or data controller. We will also cover how to identify a subject access request, why it is necessary to comply, and the timelines to beware.
Key Takeaways
- SAR request is a data subject asking for a copy of the controller’s data about the subject. A data subject can exercise this right via phone or in writing.
- When a data controller receives a SAR request, they must do a verification and fulfill it in time, resolve any disclosure conflicts, and reply securely.
- Ignoring SAR requests results in fines, court orders, and liability to pay compensation. There are exceptions where data controllers can refuse a SAR request.
What is a SAR Request?

A subject access request, sometimes known as a data subject access request (DSAR) or a data subject request (DSR), is a request by a data subject made to the data controller to release data about the data subject. Data could be in digital or paper format.
SAR requests may be formal or informal. Formal request examples include a letter addressed to the data controller or an email sent to the data controller’s official email. Informal request examples include requests made over a phone call or on social media.
Handling SAR requests properly helps businesses show their compliance with data processing principles and avoid the risks of penalties or lawsuits. It is a chance for data subjects to rectify any mistakes and for data controllers to update their records.
Why Must You Beware of Subject Access Requests?

According to Article 15 of the GDPR, the data subject shall have the right to obtain from the controller access to the personal information the controller holds about them. As provided in Article 12(3) of the GDPR, the data controller has one month within which to fulfill a SAR request.
If the data controller needs more time, they must request an extension within the initial one-month deadline. Extensions are only allowed if the SAR request is complex and it’s really needed.
Data controllers who ignore a SAR request can expect a lawsuit and a court order compelling them to fulfill the request. Courts can also award the data subject compensation in such cases.
How to Identify a Subject Access Request
There are many requests that can be directed at businesses requesting information. Sometimes it can be tough to find the SAR requests because most SAR requests do not have SAR requests explicitly stated. Here’s how to identify SAR requests easily with the following points.
- It requests their HR records
- It requests all information held about them
- It requests the personal data held by the controller
- It requests information the controller holds about them
- It requests personal data about them that the controller stores
- It requests reasons why the data controller is holding their personal data
- It requests CCTV camera footage at a certain location within a specific timeframe
- It requests emails between them and another individual within a specific timeframe
This partial list gives a head start when identifying SAR requests.
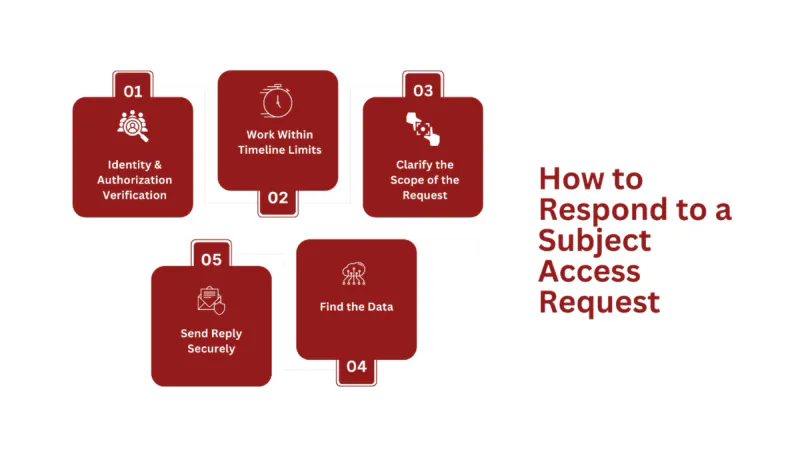
How to Respond to a Subject Access Request
Depending on how the subject access request was received, all requests should be immediately forwarded to the organization’s data protection officer (DPO) or compliance department.
Businesses using a compliance-as-a-service (CaaS) solution like Captain Compliance will have this streamlined and semi-automated system, allowing for efficiency. The DPO or compliance group will then take the following steps:
Identity/Authorization Verification
The first step is to confirm the data subject’s identity, where they make the request themselves. When someone else requests on the data subject’s behalf, the organization must confirm the authorization before fulfilling the request.
Authorization is helpful where the data subject is a child or an adult that cannot do it themselves. Verifying identity and authorization is important because delivering the data to someone not allowed access will be considered a data breach and can result in penalties.
Work Within Timeline Limits
SAR requests require prompt attention as data controllers have 30 days to fulfill the request. Where a SAR due date falls on a non-working day, there is an allowance to still be on time by fulfilling on the next working day. A trustworthy CaaS like Captain Compliance will handle these requests in no time.
Clarify the Scope of the Request
In fulfilling the request, the data controller should clarify what exactly the data subject wants. It’s possible the request is only for a specific category of data and not every data held by the controller.
Find the Data
Now you know what data is needed, the next step is to find it. A simple search of the business database should work. Some collaboration with the IT department may be necessary to search for the appropriate data.
Send Reply Securely
After finding the data and redacting any data unrelated to the requester, prepare to send a reply securely. You must obtain consent to include data unrelated to the requester in the reply. You must keep a record of the reply sent. All the above steps apply even when the reply refuses the request.
Things to include in the reply:
- Data collected
- How long has data been held, and how much longer will it be held
- Purpose of data processing
- Third parties data is shared with
- Notification of the right to rectification
- If data was used for automated processing
- If the data was used for consumer profiling
- Notification of data subject’s right to complain to the data protection authority
- Notification of the data subject’s right to seek redress in court
How Long do you have to Respond to a Subject Access Request?
The GDPR provides a one-month timeline starting when the data controller confirms the requester’s identity. Therefore, building a privacy compliance culture in your business is important so requests are promptly forwarded to the right desks.
It is possible to request an extension, but only if the data subject’s request is complex. Extensions are for another two months and cannot be further extended. You must request an extension within the initial one-month deadline.
Closing
Managing SAR requests could become a nightmare for businesses with thousands, millions, and even billions of consumers. Is there a better way? Yes.
At captain compliance, our CaaS solutions help you efficiently manage the SAR requests process, from receiving the request to fulfilling it. We ensure you are boosting your business with consumer satisfaction and meeting compliance obligations. Get in touch today!
FAQs
Who can make a SAR Request?
Any individual can make a SAR request. Data subjects can make the requests themselves or ask someone else to make the request on their behalf, with authorization. Children can also make SAR requests but need to do so through the parent who consented on their behalf during data collection or another adult with authorization.
Learn more about GDPR Data Mapping
Why is a SAR Request Necessary?
It helps businesses maintain the transparency principle by allowing data subjects to know the lawfulness and accuracy of the data the controller holds. It is an opportunity to check if the data subject needs rectification for any mistakes discovered.
Find out more about Data Compliance Solutions
What can I Ask for in a SAR Request?
Data subjects can ask for all or some categories of the data held by the controller. The controller may redact part of the data that does not relate to the data subject.
Learn More About What is a Data Inventory
Can Businesses Ignore or Refuse a SAR Request?
No. Businesses are obligated, under the GDPR, to respond to SAR requests. However, there are exceptions. They can charge a fee for multiple or complex requests.
Check What is a Compliance Officer
What are the Exceptions to Fulfilling a SAR Request?
Businesses can refuse a SAR request where fulfilling it will infringe on another individual’s right or negatively impact an ongoing investigation or inquiry. Where this is the case, the business must still send its reply within the one-month deadline.
Understand What is an Accountability Framework
What happens if a SAR Request is Ignored?
Data subjects who have ignored SAR requests can approach the court for redress. The court can issue an order to compel compliance and mandate the data controller to compensate the data subject.
As ignoring a SAR request amounts to infringing on the rights of data subjects, the data controller could be liable to a fine from the data protection authority.