
Safeguarding consumer privacy has become more important than ever. This GDPR guide offers a roadmap for businesses to comply with critical regulatory requirements in the digital age.
Our guide includes key elements of the EU GDPR, why the GDPR is important, and a clear path to successful implementation. Following these guidelines helps businesses achieve regulatory compliance, protect personal data, and build trust with consumers.
Let’s dive right in.
Key Takeaways
The GDPR applies globally, affecting all businesses that process the personal data of EU residents, underscoring the importance of establishing robust data management frameworks that align with regulatory guidelines.
Comprehending and accurately identifying the business’s role as a data controller or processor under GDPR is crucial, as these roles carry different responsibilities that directly impact compliance strategies.
The documentation and record-keeping, covering all aspects of data handling and GDPR compliance procedures, are essential not just for demonstrating compliance but also for mitigating potential risks during audits or data breaches.
Understanding the GDPR
understanding the gdpr.png

The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a compliance framework implemented by the European Union to protect consumers’ privacy and personal data. It came into effect on May 25, 2018, and has since reshaped the way businesses handle and protect personal information.
The GDPR is not limited to businesses based within the EU but extends to all entities that process data of individuals residing in the EU.
Its objectives revolve around ensuring transparency, security, and accountability in data processing while giving consumers control over their personal information.
The GDPR’s strict penalties for non-compliance underscore the importance of regulatory adherence for businesses.
A violation could result in fines up to €20 million or 4% of the firm’s global annual revenue of the previous fiscal year, whichever is higher. As such, a deep understanding and effective implementation of GDPR principles are crucial for any business operating in today’s digital environment.
Key Principles of GDPR
The foundation of GDPR lies in its key principles. They set the benchmark for data processing practices and define the rights of consumers. Here are the principal components of GDPR:
Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency: Data processing must be legal, fair, and transparent to the consumer. Clear information about the processing should be provided.
Purpose limitation: Personal data can only be collected for specified, explicit, and legitimate purposes.
Data minimization: Only the necessary data that is adequate and relevant should be collected and processed.
Accuracy: Businesses are obligated to keep personal data accurate and up-to-date.
Storage limitation: Personal data should only be kept for as long as necessary to fulfill the purpose for which it was collected.
Integrity and confidentiality: Personal data must be processed securely to ensure its protection against unauthorized or unlawful processing, accidental loss, destruction, or damage.
GDPR Applicability
The GDPR, like other data privacy regulations, has a specific scope that determines its applicability. It is designed to protect the personal data of all individuals residing within the European Union, regardless of where the data processing business is located.
Thus, its reach is global, impacting businesses outside the EU that offer goods or services to, or monitor the behavior of, EU residents.
Recognizing whether and how the GDPR applies to your business helps devise appropriate data protection strategies and fosters consumer trust. It helps businesses establish robust data management frameworks that align with regulatory guidelines, mitigating potential legal, financial, and reputational risks.
Who is Subject to GDPR?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has a comprehensive scope that extends to various entities dealing with personal data. The primary goal of GDPR is to safeguard the privacy rights of individuals within the European Union (EU), and so any business that interacts with this data is brought under its ambit.
Entities subject to the GDPR include:
Businesses within the EU: Regardless of whether the data processing takes place in the EU or not, all businesses located in the EU are subject to GDPR.
Non-EU businesses offering goods or services to EU residents: Even if a business is located outside the EU, it is still subject to GDPR if it offers goods or services to individuals in the EU.
Non-EU businesses monitoring the behavior of EU residents: Businesses that track EU residents’ online activities to predict and analyze personal preferences, behaviors, and attitudes are subject to GDPR.
Data controllers and processors: GDPR applies not only to businesses that control the data (decide the ‘how’ and ‘why’ of data processing) but also to those that process data on behalf of these controllers.
Determining Your Organization’s GDPR Obligations
GDPR Obligations.png

Determining if a business falls under GDPR is the first step toward understanding its compliance obligations.
It involves identifying whether the business interacts with the personal data of EU individuals if it offers goods or services to EU individuals, or monitors EU residents’ behavior.
The business needs to understand its role as a data controller, who sets the purpose and method of data processing, or a processor, who processes data on the controller’s behalf, each with different GDPR responsibilities.
Additional obligations may apply to businesses processing personal data on a large scale or dealing with special data categories, like health or financial data.
These can involve conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments or assigning a Data Protection Officer. Businesses should also recognize the range of personal data they process, from basic identity details to complex data like behavioral or biometric data.
Steps to GDPR Implementation
GDPR Implementation.png
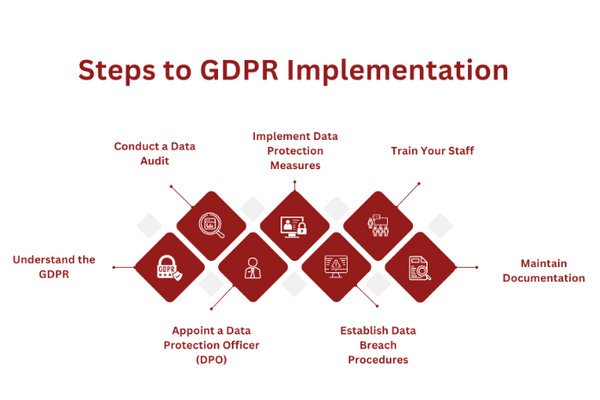
GDPR implementation is an often complex process involving organizational strategy, information technology, and legal compliance.
It requires an in-depth understanding of the regulation, a clear identification of the business’s role and obligations, and careful planning and execution.
By implementing GDPR, businesses can ensure data privacy, avoid hefty penalties, and build credibility with consumers.
Though GDPR implementation can seem daunting, breaking it down into clear, manageable steps can make the process more straightforward.
Here’s a step-by-step approach for businesses to ensure robust GDPR compliance:
Understand the GDPR
Every journey toward GDPR compliance begins with a thorough understanding of the regulation. Familiarize yourself with the GDPR’s principles, rights of data subjects, and obligations of data controllers and processors. Recognize the potential penalties for non-compliance and the importance of maintaining data privacy.
Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO)
If your business conducts large-scale data processing or processes sensitive data, you may need to appoint a DPO. This individual will be responsible for overseeing data protection strategy and GDPR compliance.
Conduct a Data Audit
Understand what data you collect, how you collect it, where it’s stored, and who has access to it. Conducting a data audit allows you to identify gaps in your current data protection mechanisms and devise strategies to address them.
Implement Data Protection Measures
Based on the data audit findings, implement appropriate measures to ensure data protection. This might include updating privacy policies, securing data storage and transfer, and improving data subject consent mechanisms.
Train Your Staff
Staff training is crucial for GDPR compliance. Ensure all staff members understand the GDPR principles and their responsibilities regarding data protection. Regular training can also help prevent data breaches.
Establish Data Breach Procedures
In the event of a data breach, quick and effective action is vital. Develop procedures to detect, report, and investigate a personal data breach. It’s important to be able to notify the relevant supervisory authority and, where necessary, the affected data subjects.
Maintain Documentation
Maintaining comprehensive records of your data processing activities is an essential aspect of GDPR compliance. Documentation should detail what data is held, where it came from, who it’s shared with, and what protective measures are in place.
Mapping GDPR Requirements to Your Business
Effectively mapping GDPR requirements to a business is an intricate process that demands a thorough knowledge of both the business’s operations and the regulatory framework.
The first step involves conducting a comprehensive review of all activities involving personal data. This includes identifying what data is collected, why it’s collected, how it’s processed, and who has access to it.
The next step is to evaluate the data processing activities against the principles and requirements set out in the GDPR. This could involve reviewing existing data protection measures, consent mechanisms, and data breach response procedures. Areas of non-compliance need to be identified, and measures to rectify these should be outlined.
Regular audits, reviews, and updates are necessary to ensure ongoing compliance because your business will evolve, and GDPR requirements will apply.
Customizing GDPR Compliance Measures
GDPR compliance should be tailored to your business’s unique needs, influenced by industry, data types, processing activities, and risk levels. A healthcare business processing sensitive data, for instance, may need stricter measures than a retail business with basic consumer data.
The risk level associated with data processing also matters. High-risk activities, such as large-scale sensitive data processing, may necessitate a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA).
Businesses with over 250 employees handling sensitive data may need a Data Protection Officer (DPO).
Documenting Your GDPR Implementation Plan
A comprehensive GDPR implementation plan is crucial for successful compliance. Documentation serves as evidence of your business’s efforts towards GDPR compliance and can be invaluable in case of audits or data breaches.
The plan should cover all the processes, procedures, and policies involved in data handling. This includes data collection methods, data storage, and security measures, data breach response procedures, and consent mechanisms.
Furthermore, accountability mechanisms need to be in place. This means recording the decision-making processes, documenting the steps taken to implement GDPR, and justifying the choices made during implementation. It’s also important to keep a record of staff training on GDPR and data protection.
GDPR Documentation and Record-Keeping
Maintaining comprehensive documentation is vital for demonstrating GDPR compliance, as the regulation emphasizes accountability. Such records help businesses evaluate and refine their data protection practices, serving as compliance proof during regulatory audits.
In the event of a data breach, these records demonstrate the business’s commitment to data protection, aiding in mitigation and legal defense. Hence, record-keeping isn’t just a formality but a crucial part of responsible data management and GDPR compliance.
GDPR Documentation Requirements
GDPR Documentation Requirements.png
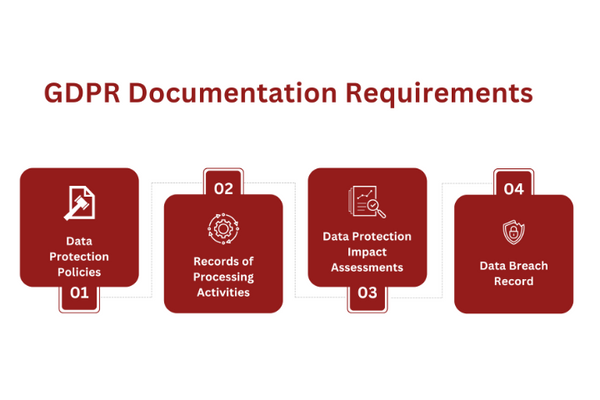
Documentation plays an integral part in the GDPR compliance journey. It assists businesses in demonstrating their adherence to the regulation’s data privacy principles and requirements.
Notably, the GDPR imposes several documentation obligations on businesses, ranging from data protection policies to records of processing activities, data protection impact assessments, and data breach records.
Data Protection Policies: Businesses must establish and document comprehensive data protection policies that outline their commitment to data privacy, data processing activities, data subjects’ rights, and procedures in place to protect data.
Records of Processing Activities (RoPA): Both data controllers and processors must maintain detailed records of their data processing activities. The RoPA should include information such as the purpose of processing, categories of data subjects and personal data, data recipients, and transfers of personal data to third countries or international businesses.
Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIA): DPIAs are required for high-risk data processing activities. They help identify and minimize data protection risks. A DPIA must document everything from the nature, scope, and purpose of data processing to the risks it presents to data subjects and the measures in place to address those risks.
Data Breach Records: In the unfortunate event of a data breach, businesses must document all details, including the nature of the breach, the categories and number of data subjects affected, the possible consequences, and the measures taken to mitigate the breach.
Conducting Regular GDPR Compliance Assessments
Compliance assessments, also known as compliance audits, are systematic evaluations of a business’s adherence to regulatory guidelines. In the context of the GDPR, a compliance assessment involves reviewing the data processing activities of a business, its data protection measures, and its documentation practices, among other elements, to ensure alignment with GDPR requirements.
These assessments are crucial in verifying that businesses are implementing the GDPR’s principles and maintaining them effectively over time.
Importance of Ongoing Compliance Monitoring
Regular GDPR compliance assessments are crucial for businesses to ensure that they continually adhere to GDPR requirements, regardless of changes in their data processing activities, organizational structure, or the external regulatory environment.
Regular assessments help businesses stay ahead of potential data protection issues and mitigate risks associated with data processing. They provide an opportunity to detect and rectify non-compliance early before it escalates into a data breach or attracts penalties from regulatory authorities.
Assessing GDPR Compliance Effectiveness
Conducting GDPR compliance assessments may involve internal audits, self-assessments, or engaging external experts. The choice depends on the complexity of a business’s data processing activities, resources, and risk exposure.
Internal audits can be a good starting point for medium-sized businesses. These audits should review the business’s data processing activities, data protection measures, consent mechanisms, and documentation practices, among other aspects.
Self-assessments can be a cost-effective method for smaller businesses. Several tools and checklists are available to guide businesses through the process. These assessments should be conducted regularly and honestly, with a focus on identifying gaps and making improvements.
For businesses processing large volumes of personal data, particularly sensitive data, or for those with complex data processing operations, engaging external experts like Captain Compliance for a GDPR audit can be a wise investment. These experts can provide a fresh, unbiased perspective and help the business navigate the complexities of the GDPR.
Dealing with GDPR Non-Compliance
Even with the best plans and intentions, instances of GDPR non-compliance may occur. Businesses must understand how to identify, address, and learn from these instances to prevent them from recurring in the future.
Equally important is acknowledging the potential consequences of non-compliance, both to motivate continued adherence to GDPR and to inform response strategies when non-compliance is detected.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
The consequences of GDPR non-compliance can be severe and multifaceted, impacting businesses on legal, financial, and reputational fronts.
Legally, businesses found to be non-compliant with GDPR may face regulatory penalties. These can range up to €20 million or 4% of the business’s total annual global turnover of the preceding fiscal year, whichever is higher.
Beyond regulatory fines, businesses may face indirect costs such as legal fees, potential lawsuit settlements, and the cost of implementing emergency remediation measures.
Reputationally, the impact can be even more devastating. Data breaches resulting from GDPR non-compliance can significantly damage consumer trust, leading to a loss of consumers and negatively impacting the business’s market position.
Furthermore, negative media attention could harm the business’s image, making attracting new consumers, partners, or talented employees harder.
Remediation and Corrective Actions
When GDPR non-compliance is identified, businesses should take the following steps to address and remediate the issue:
Identify the Cause: Understand the root cause of the non-compliance. Was it a lack of knowledge, a procedural failure, or a technical glitch?
Implement Corrective Measures: Depending on the cause, implement the necessary corrective measures. This could involve technical fixes, process changes, or additional staff training.
Update Processes and Policies: If the non-compliance was due to outdated or insufficient processes or policies, these need to be updated to align with GDPR requirements.
Address Data Subject Complaints: If the non-compliance has led to data subject complaints, these need to be addressed promptly and effectively. This may involve explaining the issue to the affected consumers, apologizing, and outlining the steps taken to prevent recurrence.
Report and Respond to Breaches: In the case of a data breach, businesses must report the breach to the relevant supervisory authority within 72 hours of becoming aware of it. They should also inform the affected data subjects without undue delay.
Review and Improve: Regularly review compliance measures to identify potential weaknesses and areas for improvement. Use instances of non-compliance as opportunities for learning and improvement.
Closing
Embarking on the path to GDPR compliance might seem daunting, but it becomes manageable with a structured approach and the right resources. Remember, achieving GDPR compliance is not a one-time task. It’s a continuous journey that calls for consistent commitment to data privacy principles.
So, what is your next move? Use the insights from this guide to create a personalizedregulatory compliance strategy and start integrating data privacy into your business operations.
Captain Compliance can significantly simplify this process for you. Our services are designed to guide your business through every stage of GDPR compliance. Start your GDPR compliance journey with us today, and make data privacy a fundamental part of your business, fostering trust with consumers in today’s data-centric world.
FAQs
What are the key changes brought about by the GDPR?
The GDPR brought about several key EU data protection changes, including enhanced rights for individuals, such as the right to be forgotten and the right to data portability, along with stricter consent requirements for data processing and potentially hefty fines for non-compliance.
Contact our team of experts today for a comprehensive understanding and actionable strategies to ensure your business is fully compliant.
How often should a business conduct a GDPR compliance assessment?
While the GDPR defines no set frequency, best practices suggest that businesses should conduct a GDPR compliance assessment at least once a year. However, it’s also advisable to conduct an assessment any time there are significant changes in business operations, data processing activities, or the regulatory environment.
Learn more about GDPR compliance requirements here.
How does GDPR impact businesses outside the EU?
The GDPR has a broad territorial scope and applies to any business, regardless of its location, that processes the personal data of individuals in the EU. This includes businesses that offer goods or services to individuals in the EU or that monitor the behavior of individuals in the EU.
If your business operates outside the EU but handles the personal data of EU residents, get in touch with us to understand your obligations and devise a solid GDPR compliance strategy.
What is the role of a Data Protection Officer (DPO) under the GDPR?
The DPO oversees a business’s data protection strategy and its implementation to ensure compliance with GDPR requirements. The DPO acts as a point of contact for data subjects and the supervisory authority and must be involved in all issues related to the protection of personal data.
If your business needs to appoint a DPO, learn more about DPOaas here.