
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has revolutionized individual privacy by granting consumers increased data subject rights.
Under the GDPR, individuals have gained improved control over their personal information. These rights empower consumers to manage how their data is collected, processed, and stored by businesses. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the key data subject rights established by the GDPR, such as the right to access, rectify, and erase personal data, and more.
You will also learn how to handle sensitive consumer data, avoid hefty fines for non-compliance and take steps toward getting your business in line with regulation standards.
What is the General Data Protection Regulation?
What is the General Data Protection Regulation.png

The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a comprehensive data protection law that took effect in May 2018, replacing the Data Protection Directiveof 1995. It is designed to harmonize and strengthen data protection regulations within the European Union (EU) and to protect the privacy rights of individuals.
The EU GDPR also applies to businesses outside the EU that process the personal data of EU residents.
The primary purpose of the GDPR is to give individuals greater control over their personal data and to enhance their privacy rights. It introduces a set of principles and requirements that businesses must follow when processing personal data.
The regulation aims to ensure that individuals are aware of and can exercise their rights regarding the collection, use, and storage of their personal information.
The GDPR sets out several key objectives. First and foremost, it emphasizes the importance of obtaining explicit and informed consent from consumers before collecting their personal data.
It also emphasizes the need for businesses to provide transparent and clearinformationabout how data is used and to implement appropriate security measures to protect personal information.
Another essential objective of the GDPR is to strengthen the rights of individuals regarding their personal data. It introduces a range of data subject rights, including the right to access, rectify, and erase personal data, as well as the right to restrict processing and object to certain types of data processing.
One of the first steps your business can take toward GDPR compliance is understanding the scope of data subject rights:
What are the GDPR Data Subject Rights?
GDPR data subject rights grant individuals a range of powerful tools to protect their privacy and control how their personal information is handled by businesses. These rights are essential in safeguarding individual privacy and promoting transparency in the digital era.
Here are some of the key principles underlying GDPR data subject rights:
Right to Access: Individuals can obtain confirmation from businesses about whether their personal data is being processed and, if so, to access that data and receive relevant information about its use.
Right to Rectification: Individuals can request the correction of inaccurate or incomplete personal data, ensuring that the information held by businesses is up-to-date and reliable.
Right to Erasure: Also known as the “right to be forgotten,” individuals can request the deletion of their personal data under certain circumstances, such as when the data is no longer necessary or when consent is withdrawn.
Right to Restrict Processing: Individuals can request the limitation of the processing of their personal data in certain situations, providing them with more control over how their information is used.
Right to Object: Individuals have the right to object to the processing of their personal data, including for direct marketing purposes, and businesses must cease processing unless they can demonstrate compelling legitimate grounds.
Right to Data Portability: Individuals can receive their personal data in a structured, commonly used, and machine-readable format, allowing them to transfer it to another organization if desired.
The significance of these data subject rights lies in empowering consumers to take charge of their personal data. They provide individuals with greater transparency and control over how their information is collected, stored, and used by businesses. Learn more about the scope of the GDPR and also which individuals are covered by the GDPR rights.
Key Aspects of Consumers’ Right to Information and Transparency
Key Aspects of Consumers Right to Information and Transparency.png
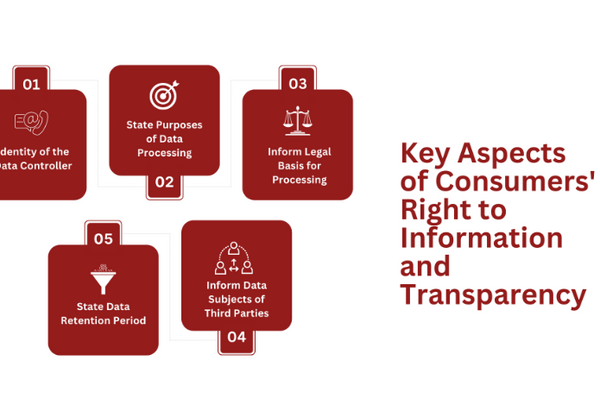
The data subject’s right to be informed is a fundamental aspect of the GDPR. It requires businesses to provide consumers with clear and concise information about the processing of their personal data.
This right ensures that consumers know how their data is being collected, used, and protected, allowing them to make informed decisions about their privacy.
To comply with the right to information, businesses must provide the following specific details to data subjects:
Identity of the Data Controller
Individuals should be informed about the identity of the organization or entity responsible for processing their personal data. This includes contact information and, if applicable, the details of the organization’s representative.
State Purposes of Data Processing
Businesses must clearly state the purposes for which personal data is being processed. Whether it is for contract fulfillment, legal obligations, legitimate interests, or explicit consent, individuals have the right to know why their data is being collected and used.
Inform Legal Basis for Processing
Businesses must inform individuals of the legal basis for processing personal data. This could be consent, the performance of a contract, compliance with a legal obligation, protection of vital interests, or other legitimate interests pursued by the data controller or a third party.
Inform Data Subjects of Third Parties
Data subjects should be aware of any third parties or categories of recipients with whom their personal data is shared. This includes data processors, service providers, or other organizations involved in data handling.
State Data Retention Period
Individuals have the right to know how long their personal data will be stored by the data controller or the criteria used to determine the retention period.
By providing all this information, your business ensures transparency and empowers individuals to exercise their rights effectively. We have a guide on SAR requests, which are requests done by data subjects regarding their rights for more information.
Right to Access & Rectify Inaccurate Personal Data Explained
The data subject’s right to access and rectify inaccurate personal data is a fundamental aspect of the GDPR. It allows individuals to obtain confirmation from organizations as to whether their personal data is being processed and, if so, to access that data.
This right enables individuals to review the information held about them and ensure its accuracy and relevance.
Individuals can submit a request to the business that holds their data, specifying the information they would like to access. The business must then provide a copy of the requested data in a commonly used electronic format (such as a PDF or Excel file).
If individuals discover inaccuracies or incompleteness in their personal data, they can request rectification. After communicating the specific corrections needed, the business must then promptly update the data and inform any third parties with whom the data has been shared.
Implementing the right to access and rectification in your business involves the following steps:
Establish a Request Process
Create a clear and accessible procedure for individuals to submit requests for accessing their personal data. This can be done through an online form or by providing contact information for submitting requests.
Verify the Identity
Implement measures to verify the identity of the individual making the request to ensure the security and confidentiality of personal data.
Using a confirmation email is a common and budget friendly way to ask the consumer to click on a verification link to proceed with the request. More complicated verification methods include an SMS system or 2FA (two-factor authentication).
Provide Access to Personal Data
Upon receiving a valid request, your business must provide the individual with a copy of their personal data in a structured, commonly used, and machine-readable format. Include supplementary information alongside the raw data, that helps the user access their requested information.
Depending on the nature of the request and the systems in place, you may provide access through secure online accounts, encrypted email attachments, or secure file transfer protocols.
Enable Review of Personal Data
Ensure that the provided personal data is clear, understandable, and presented in a comprehensive manner, allowing individuals to review the information and understand its purpose and processing.
Facilitate Rectification Requests
Establish a mechanism for individuals to request the rectification of inaccuracies or incompleteness in their personal data. Promptly update the data and communicate the changes to any relevant third parties.
Maintain Audit Trails
Keep records of access and rectification requests, including details of the requests, actions taken, and any communication with the individuals involved. This ensures compliance and accountability.
By implementing these steps, your business can effectively uphold the data subject’s right to access and rectification, demonstrating a commitment to data accuracy. Learn more about our data compliance solutions.
Guidelines on Right to Data Erasure
Guidelines on Right to Data Erasure .png

The data subject’s right to erasure, also known as the “right to be forgotten,” allows individuals to request the deletion or removal of their personal data under specific circumstances. However, it is important to note that the right to erasure is not absolute and is subject to certain obligations and exceptions.
When individuals exercise the right to erasure, organizations have obligations to fulfill their requests in a timely manner.
Suppose the request is valid and meets the criteria outlined in the GDPR. In that case, organizations must promptly delete personal data and take reasonable steps to inform any third parties with whom the data has been shared.
This ensures that personal data is securely and permanently removed from the organization’s systems and those of any external recipients.
There are several grounds for requesting the erasure of personal data, including:
When the personal data is no longer necessary for the purposes for which it was collected or processed.
When consumers withdraw their consent to process their data, there is no other legal basis for the processing.
When consumers object to the processing, there are no overriding legitimate grounds for the processing as per Article 17.
When personal data has been unlawfully processed.
When the erasure is required to comply with a legal obligation.
As for exceptions – businesses are not obligated to erase personal data in cases where processing is necessary certain reasons such as:
Exercising the right tofreedom of expression and information
Compliance with a legal obligation
Performance of a task carried out in the public interest
Exercise of official authority, or the establishment, exercise, or defense of legal claims
Understanding the Right to Restrict Processing
The GDPR grants data subjects the right to restrict processing and the right to object to certain types of processing. The exercise of these rights is subject to specific conditions and requirements.
The right to restrict processing allows individuals to request the limitation of the processing of their personal data. This means that while the processing is restricted, the data can be stored without further processing unless with the individual’s consent or for specific legal purposes.
Individuals can exercise this right under various circumstances, including when the accuracy of the personal data is contested, the processing is unlawful, or the data is no longer needed for its original purpose but is required for legal claims.
Right to Object to Data Processing
The right to object enables individuals to object to certain types of processing activities. This includes processing for direct marketing purposes and processing based on legitimate interests or the performance of a task carried out in the public interest.
When individuals object to the processing, the organization must stop processing their personal data unless they demonstrate compelling legitimate grounds that override the individual’s interests, rights, and freedoms.
Here are some examples of situations where data subjects can exercise these rights:
Requesting a restriction on processing while verifying the accuracy of their personal data.
Objecting to the processing of personal data for direct marketing purposes.
Objecting to the processing based on legitimate interests, such as in cases where the individual’s fundamental rights and freedoms outweigh the organization’s interests.
Requesting a restriction on processing when the personal data is no longer needed, but the data subject requires it for the establishment, exercise, or defense of legal claims.
By recognizing and respecting the rights to restrict processing and object to processing, businesses allow consumers to have a say in how their personal data is used and ensure that their preferences are considered.
Right to Data Portability Explained
Right to Data Portability Explained.png

The data subject’s right to data portability is a significant provision under the GDPR, granting individuals the right to receive their personal data from organizations in a structured, commonly used, and machine-readable format.
This right allows individuals to obtain and reuse their personal data for their own purposes across different services or with other organizations.
It also enables consumers to access and transfer their data easily, facilitating the seamless movement of personal data between service providers or platforms. By receiving their personal data in a machine-readable format, individuals can utilize and integrate their data with other applications, services, or systems according to their preferences.
How to Comply With GDPR’s Data Subject Rights
Regulatory compliance with GDPR’s data subject rights is crucial for businesses to not only avoid legal consequences but also establish their reputation on the free market.
To ensure compliance, businesses should establish robust policies, procedures, and technical measures that align with the principles and requirements of the GDPR.
Implementing appropriate policies is essential to outline how the organization handles personal data. These policies should cover aspects such as consent management, data retention and deletion, data access and rectification processes, and mechanisms for handling data subject requests and complaints.
Regularly reviewing and updating these policies based on evolving privacy regulations and industry best practices is crucial. Learn more about how to protect your business from non compliance fines
Here are some best practices/steps businesses should take to ensure compliance with data subject rights:
Develop andregularly update comprehensive policies that address data subject rights and privacy-related matters.
Establish clear procedures for handling data subject requests, including verification processes and response timelines.
Train employees on data subject rights, their responsibilities, and proper handling of requests.
Implement technical measures to safeguard personal data, including encryption and access controls.
Regularly review and update consent mechanisms to ensure compliance with GDPR requirements.
Maintain documentation of data subject requests, actions taken, and any disclosures or communications made.
Conduct periodic assessments to evaluate the organization’s compliance with data subject rights and privacy regulations.
Establish a mechanism to address data subject complaints and ensure timely resolution.
Stay updated on changes to privacy regulations and industry best practices to adopt policies and procedures accordingly.
Foster a privacy-aware culture within the organization and prioritize protecting personal data.
By following these best practices and steps, your business is on the right track to enhance its compliance with GDPR’s data subject rights, mitigate privacy risks, and maintain a positive relationship with consumers.
How to Handle Data Subject Requests
Data subject requests refer to the requests made by individuals to exercise their rights under the GDPR.To handle data subject requests effectively, organizations should establish clear and streamlined systems in place.
Additionally, businesses must keep proper records of the requests received, actions taken, and any communications made with the data subject.
Here are the steps in the process of handling data subject requests:
Designate a point of contact or a team responsible for handling data subject requests.
Establish procedures to verify the identity of the individuals making the requests.
Acknowledge receipt of the request promptly and within the required timeframe.
Review the request and assess its validity and compliance with the GDPR.
Collect and collate the relevant personal data or information requested.
Prepare a comprehensive response addressing the specific request and providing necessary information.
Ensure accuracy and transparency in the response, explaining the actions taken or the reasons for any limitations.
Maintain proper records of the requests received, actions taken, and any communication with the data subject.
Continuously review and update the procedures for handling data subject requests based on feedback and evolving regulations.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with GDPR data subject rights can have significant consequences for organizations, including reputational damage, regulatory fines, and legal actions.
Firstly, non-compliance can lead to severe reputational damage, as consumers are increasingly concerned about the privacy and security of their personal data.
If an organization is found to have mishandled data subject rights, it can lose the trust and confidence of its customers, resulting in a damaged brand reputation and potential loss of business.
Additionally, regulatory authorities can impose substantial fines for GDPR violations. The fines can be up to 4% of annual global turnover or €20 million. Organizations that fail to comply with data subject rights risk facing these significant financial penalties, which can have a substantial impact on their operations and financial stability.
Lastly, non-compliance with GDPR data subject rights can expose organizations to legal actions. Individuals whose data privacy rights have been infringed upon could seek legal recourse, including initiating lawsuits or joining class-action lawsuits.
Closing
Getting a complete understanding of GDPR data subject rights is a daunting task because it can be complicated! After understanding the GDPR framework, taking action for your business to accommodate GDPR is where our data compliance service can come in handy.
Captain Compliance offers a wide array of compliance services to help your business navigate the complexities of GDPR data subject rights and achieve compliance. From developing privacy policies to establishing processes for handling data subject requests, Captain Compliance can provide practical advice tailored to the specific needs of your business.
Contact us today to get help implementing the appropriate policies, procedures, and technical measures to ensure compliance with data subject rights!
FAQs
Difference Between Right to Access & Right to Data Portability?
The right to access allows individuals to obtain a copy of their personal data and information about how it is being processed.
On the other hand, the right to data portability goes a step further, enabling individuals to receive their personal data in a structured, commonly used, and machine-readable format, allowing for easy transfer to another organization or service.
Here is the best GDPR software to ensure you have full GDPR compliance
Are there Exceptions to the Right to Erasure?
Yes, there are exceptions to the right to erasure. The right to erasure is not absolute and can be limited in certain circumstances. Suppose the processing of personal data is necessary for exercising the right of freedom of expression and information.
In that case, compliance with a legal obligation, the establishment, exercise, or defense of legal claims, and the right to erasure may not apply.
Discover all about the CPRA’s right to data deletion
Are There Fees for Data Subject Requests?
Organizations generally cannot charge a fee for fulfilling data subject requests unless the requests are unfounded, excessive, or repetitive.
However, if a request is manifestly unfounded or excessive, organizations may charge a reasonable fee taking into account administrative costs or refuse to act on the request altogether.
Check out our data compliance services!
Does my Business Need Cookie Consent?
Yes, your business likely needs cookie consent. Implementing a robust cookie consent mechanism not only helps you adhere to legal requirements but also enhances trust between your business and its customers.
Regardless of the size or nature of your business, incorporating cookie consent is essential to ensure that your online activities are compliant and privacy-conscious.